Sunday, October 29, 2023
Podcast 2 of 3 Creating a Program - Mem-ExSpan, memspan's
Sunday, October 15, 2023
The Erratic Tik - Tok Brain Embraces Entertainment
To continue my ongoing discussion of “Solid learning factors”, including focus, many articles today discuss concerns about the current 1-minute Tik Tok brain instilling erratic focus for our young people.
Poor focus interferes with listening integration sorely needed for sequencing, learning, retaining and applying new material.
Historical Impact:
Subsequently, it stands to reason, that speaking, looping, puppet faces might provoke staring, leading to focus.
Professor Brown becomes a local “hit" for a few people, so decided to hike to the New York Stage with a backpack of puppets.
Although it took him awhile to travel such a distance, he was well
received on local city small vaudeville stages, making some income to feed his
family. They have been surviving on buttermilk and popcorn in rural
1923 - 1955 “Doc”
Brown’s two sons, Fay and Foy E, are soon carving wooden faces like their
father had done earlier. They perform for local
1935 – 1955 Roughly
in the same time frame, Ventriloquism was becoming a hit comedy act for night
club entertainment on the East and West coast areas. Many tried to perform in
The final outcome of the “Peers and Puppets” experiment was
that team students’ TIED with the puppetry methods. Both groups focused on a
peer role model and the teaching cloth puppet. All win-wins.
Jan meets with Foy, in 1972, purchases two ventriloquist dummies, and soon is applying puppetry comedy routines for advertising with her three children as musical and speaking performers. It becomes a summer activity for the three children, who are musical.
Saturday, September 23, 2023
Banging Your Head Against the Wall
Sometimes it feels like we are “banging our heads against a wall” when people are not listening to us. They often ask questions just explained.
Unfortunately, many can only focus and follow one step holistically at a time, and cannot detect issues within the entire sequential procedure. Slow in procedural thought, “one unit at a time-piecemeal”, they become over-whelmed with step-wise instructions.
This unpredictable mind set creates a flow of errors that is both time-consuming and costly to reformulate properly.
Today’s work projects often employ three to five individuals, at high cost inefficiency, to accomplish a simple procedure.
The following alarming story was recently related to me by a hospital book-keeper, as an incorrect coding entry had been taking a year of our involvement to resolve the accounting/mis-coded issue.
Without productive efficiency, projects fail with faulty detail. All work operations are a series of ordered details to be completed correctly, systematically, with full accountability.
Any work chain with too many links can break down to error laden inefficiency.
Actual Medical Scenarios:
Inversely, there were several people at the Medicare side to conduct the same, expensive, time laden, data entry chain link process to finally correct the claim.
Then the doctor confronted with the dire results, requiring
immediate surgery, lucky for me with my high listening-auditory-coding
capability, I recognized the problem immediately, and confronted her with
“these photos are not my newly filmed records”.
Of course, the doctor double checked my file, was embarrassed, and apologized, as I have nearly perfect eyesight.
Obviously, I could have gone through unnecessary eye surgery, not to mention, the time involvement, and the anxiety-stress incurred.
Subsequently, this circumstance could have been avoided by pre-testing the listening capability of future technician applicants.
Erland, J. K. (February 1986, 1989).Contrapuntal thinking
and the definition of sweeping thinking).
Monday, September 4, 2023
What is Common Sense and Logic? Why Do We Need It?
The term “common sense” always baffled me, as I was growing up; individuals said I had amazing “common sense,” and tackled problems wisely. This leads me to the discourse, “what is common sense, exactly?”
A Basic Conclusion for “Common Sense”
would be simply: “Don’t step in
front of an oncoming car.” “Avoid lightning strikes”, or Don’t eat strange
reptiles,” as the outcomes are obvious to most people.
My Personal Conclusion “Common Sense”: It may be the ability to flood the mind rapidly, with a variety of options, and then make the best choice rationally, not emotionally, in any given moment.
If
it is an emergency, we are forced to think fast. Otherwise, we can carefully
weigh in our personal options – pros and cons in a logical manner.
Impulsivity and “Common Sense”: a fast, risky, choice is made without any
deep thought. An individual may realize they made it, but cannot fathom how
they reached that conclusion. or understand the eventual consequences.
Often, this line of thinking is habitual,
and this decision-making pattern continues throughout their lives.
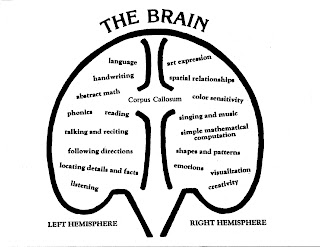
How the Brain is Involved
In trying to understand the role of “Common Sense” cognitively, we can realize that the cerebellum is the master or “muscle,” doing the brain’s work load, whereas, the cerebrum is the “thought control”.
And, additionally, each individual has their own unique electrical synapse
system created through their learning experiences.
Therefore, we should desire interconnecting
them in concert for optimal whole brain thinking leading to logical thinking
and decision making.
We can create “Choice Architecture” [1] In making decisions that permeate our wired brains.
We can use tools, or options,
to create common sense through logical thought processes, for making decisions
with desirable outcomes.
Device Screen Options
We can apply a unique assortment of options
with our devices’ screens to give us the answers we seek.
Consider not being distracted by the
constant advertising on our screens, so we can maintain our thought flow and
make optimum decisions, or levels of thought operations.[2]
My former article on “Focus” reiterated the Tik Tok - UTube data findings[3] that many have developed a “one-minute” brain attention span.
This recent article for
“Family and Tech” in the Wall Street Journal, reveals that “UTube one- minute “Shorts”
give kids short, thrill bursts, making it harder to pull away” Brains are being
short-circuited, camouflaging any possible “Common Sense” or logic.
As many innovators spot this issue, they
clamor to come up with immediate, money-making solutions. This data is rapidly
absorbed into marketing advertisements.
This becomes a “Hay-Day” for marketing and
screens, as our brains’ logical capabilities wither.
Takeaway, thought-provoking point to
ponder:
If we have a uniquely wired brain, laden with experiential, ethics, and skills learning, making our formulated choice options based on this factor, yet, data mining shows that many can focus only for one-minute or so, what can (or will) alter this anomalous paradigm?
Are we
making choices based on a short-circuited brain, lacking logic?
[1] Johnson, Eric (2021). The Elements
of Choice.
[2] Erland, J. K. (1989). Hierarchy of Thinking
Model.
[3] Julie Jargon. (August 15, 2023). “An Antidote
for ‘Tik Tok Brain’ Has Also Become a Problem” The Wall Street Journal.